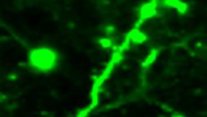
Multiphoton microscope: neurons and axons in the brain
Understanding the brain requires recording the activities of a large number of neurons. To achieve this goal requiresImaging technology with micron-level resolution, deep penetration and in vivo measurement is required. Multiphoton laser scanning microscope is currently the main technology. The adaptive femtosecond laser source developed by us reduces the optical power of multiphoton laser scanning microscope (two-photon and three-photon) to 1/30 of the original, so as to increase the imaging speed, the field of view, and the imaging depth, and reduce the laser cost. This work was published in the Nature Methods and was reported by Nature, Science, OPN, OSA Plenary talk, SPIE Hot Topic, etc. It is a key technology to break the bottleneck of neuronal imaging.
Related publications:
1. B. Li, C. Wu, M. Wang, K. Charan, and C. Xu, “An adaptive excitation source for high speed multiphoton microscopy,” Nature Methods, vol. 17, pp. 163-166, 2020.
2. M. Wang, C. Wu, D. Sinefeld, B. Li, F. Xia and C. Xu, “Comparing the effective attenuation lengths for long wavelength in vivo imaging of the mouse brain,” Biomedical Optics Express, vol. 9, pp. 3534-3543, 2018.
3. F. Xia, C. Wu, D. Sinefeld, B. Li, Y. Qin and C. Xu, “In vivo label-free confocal imaging of the deep mouse brain with long-wavelength illumination,” Biomedical Optics Express, vol. 9, pp. 6545-6555, 2018.