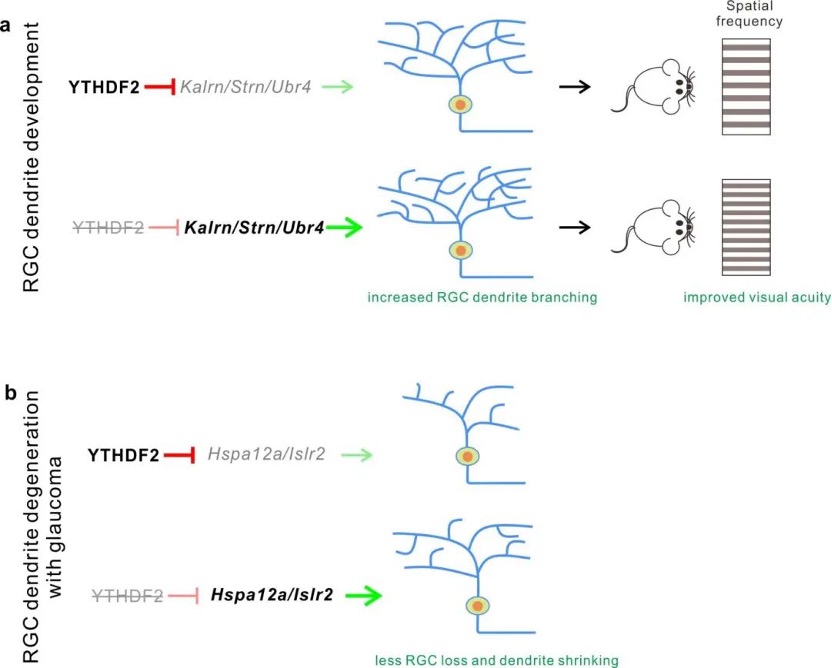
The precise control of growth and maintenance of the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) dendrite arborization is critical for normal visual functions in mammals. However, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we find that the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) reader YTHDF2 is highly expressed in the mouse RGCs. Conditional knockout (cKO) of Ythdf2 in the retina leads to increased RGC dendrite branching, resulting in more synapses in the inner plexiform layer. Interestingly, the Ythdf2 cKO mice show improved visual acuity compared with control mice. We further demonstrate that Ythdf2 cKO in the retina protects RGCs from dendrite degeneration caused by the experimental acute glaucoma model. We identify the m6A-modified YTHDF2 target transcripts which mediate these effects. This study reveals mechanisms by which YTHDF2 restricts RGC dendrite development and maintenance. YTHDF2 and its target mRNAs might be valuable in developing new treatment approaches for glaucomatous eyes.

paper link: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35179492/