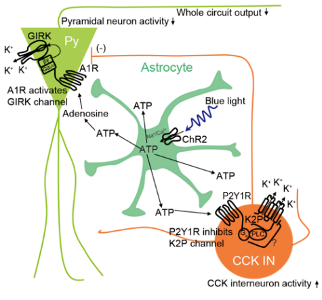
An article titled "Glia-derived ATP inversely regulates excitability of pyramidal and CCK-positive neurons" published online on January 27, 2017 in Nature Communication, found that the intracellular calcium and extracellular ATP increase, after the activation of astrocytes through optogenetic methods in the CA1 area of the hippocampus. The frequency of action potential firing of excitatory neurons decreased, but that of CCK positive inhibitory neurons increases. The activity of other types of inhibitory neurons is not affected. The mechanism of this differential regulation is due to the different receptor (adenosine A1 receptor or P2Y1 receptor) and the signal pathway (G protein coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels or two-hole potassium channel (K2P)) for ATP and related metabolite adenosine secreted by astrocyte. Finally, the excitability of the entire circuit is reduced by reducing the excitability of excitatory neurons and increasing the excitability of inhibitory neurons. This research work shows that astrocytes have a complex and delicate regulation effect for neural circuits, and ATP derived from astrocytes has a balanced and stable effect on the excitability change of the hippocampal circuit under various pathophysiological conditions, suggesting that ATP has potential neuroprotective effects and medicinal values.