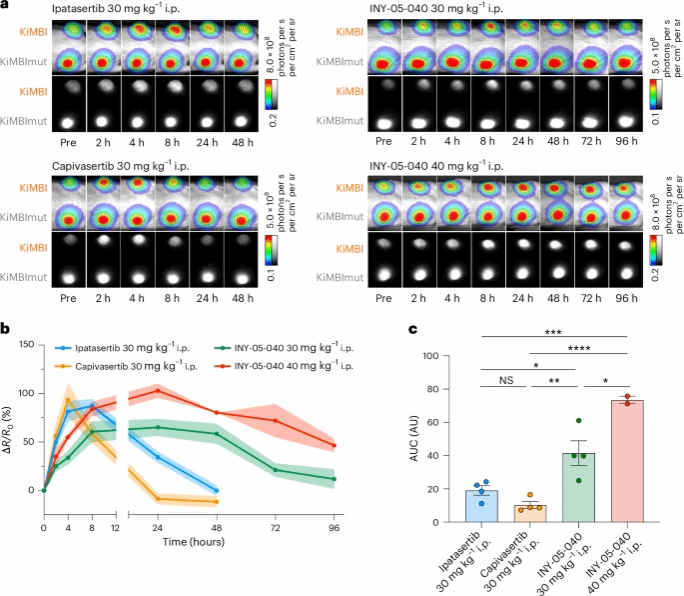
Measuring pharmacodynamics (PD)—the biochemical effects of drug dosing—and correlating them with therapeutic efficacy in animal models is crucial for the development of effective drugs but traditional PD studies are labor and resource intensive. Here we developed a kinase-modulated bioluminescent indicator (KiMBI) for rapid, noninvasive PD assessment of Akt-targeted drugs, minimizing drug and animal use. Using KiMBI, we performed a structure–PD relationship analysis on the brain-active Akt inhibitor ipatasertib by generating and characterizing two novel analogs. One analog, ML-B01, successfully inhibited Akt in both the brain and the body. Interestingly, capivasertib, ipatasertib and ML-B01 all exhibited PD durations beyond their pharmacokinetic profiles. Furthermore, KiMBI revealed that the PD effects of an Akt-targeted proteolysis-targeting chimera degrader endured for over 3 days. Thus, bioluminescence imaging with Akt KiMBI provides a noninvasive and efficient method for in vivo visualization of the PD of Akt inhibitors and degraders.

paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41589-025-01846-y
Research Briefing: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41589-025-01847-x