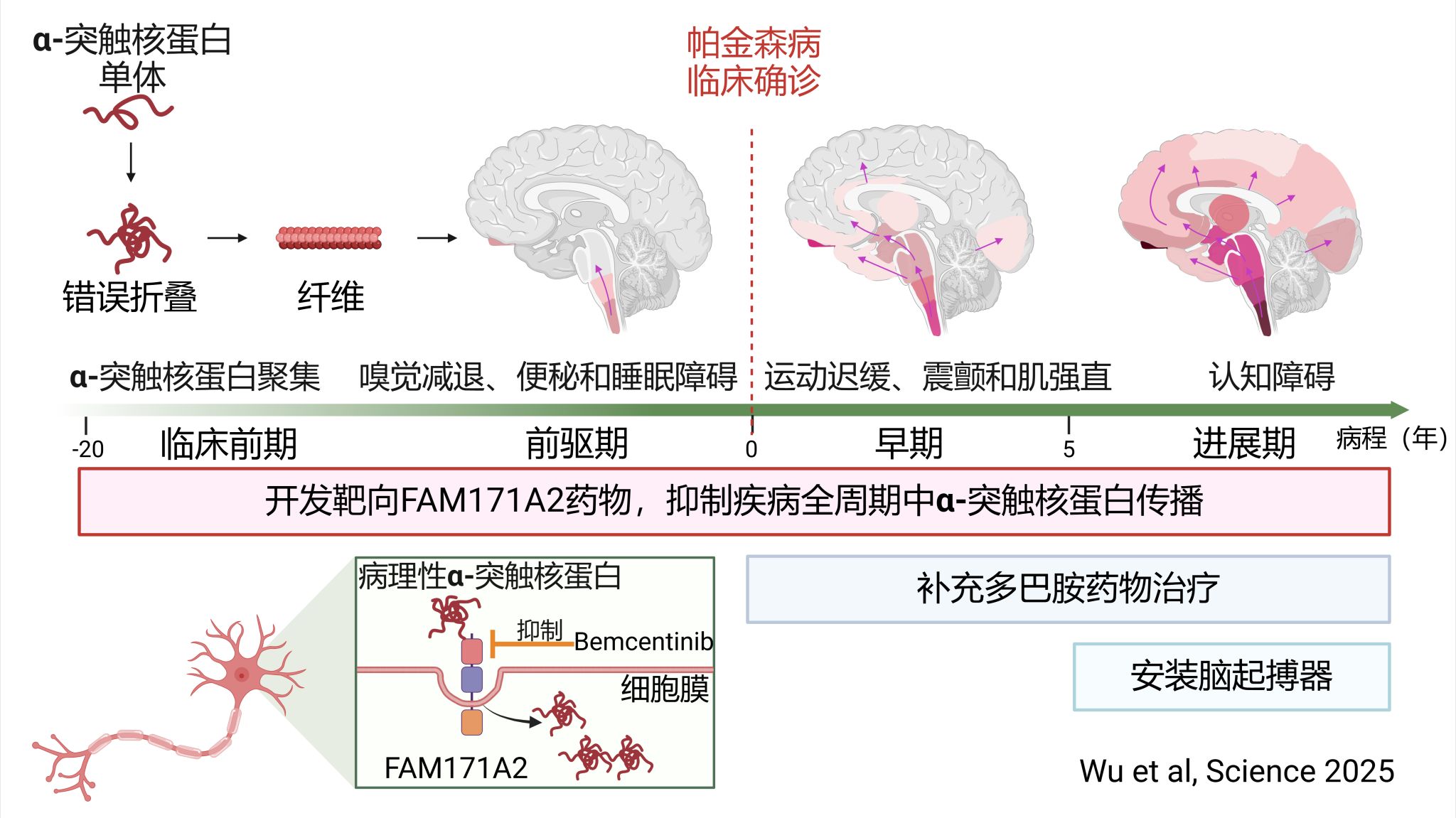
Neuronal accumulation and spread of pathological α-synuclein (α-syn) fibrils are key events in Parkinson's disease (PD) pathophysiology. However, the neuronal mechanisms underlying the uptake of α-syn fibrils remain unclear. In this work, we identified FAM171A2 as a PD risk gene that affects α-syn aggregation. Overexpressing FAM171A2 promotes α-syn fibril endocytosis and exacerbates the spread and neurotoxicity of α-syn pathology. Neuronal-specific knockdown of FAM171A2 expression shows protective effects. Mechanistically, the FAM171A2 extracellular domain 1 interacts with the α-syn C terminus through electrostatic forces, with >1000 times more selective for fibrils. Furthermore, we identified bemcentinib as an effective blocker of FAM171A2–α-syn fibril interaction with an in vitro binding assay, in cellular models, and in mice. Our findings identified FAM171A2 as a potential receptor for the neuronal uptake of α-syn fibrils and, thus, as a therapeutic target against PD.
paper link: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adp3645