The small GTPase Rac1 contributes to extinction of aversive memories of drug withdrawal by facilitating GABAA receptor endocytosis in the vmPFC. J Neurosci. 37(30):7096-7110.
The aversive memory associated with drug withdrawal can evoke motivational and/or emotional states that lead to compulsive drug taking. Our research focuses on synaptic plasticity in aversive memory, which contributes to the understanding of the neural mechanisms of opioid addiction and promotes the translation from basic research to clinical application and to the potential therapies for drug addiction.
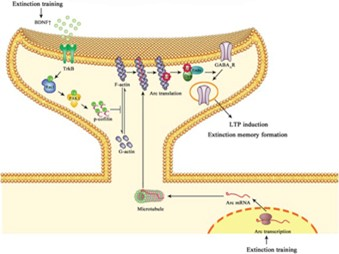
We report that extinction training activates Rho GTPase Rac1 in a BDNF-dependent manner in the vmPFC. Activate Rac1 induces synaptic actin polymerization via activating Pak1-cofilin signal pathway. Meanwhile, extinction training also results in Arc mRNA transcription. Arc mRNA is then translocated at dendritic spines through actin polymerization-dependent machinery. Within the dendritic spines, Arc proteins are rapidly translated and then form a complex with dynamin to facilitate GABAA endocytosis, thereby leading to LTP induction and CPA extinction.