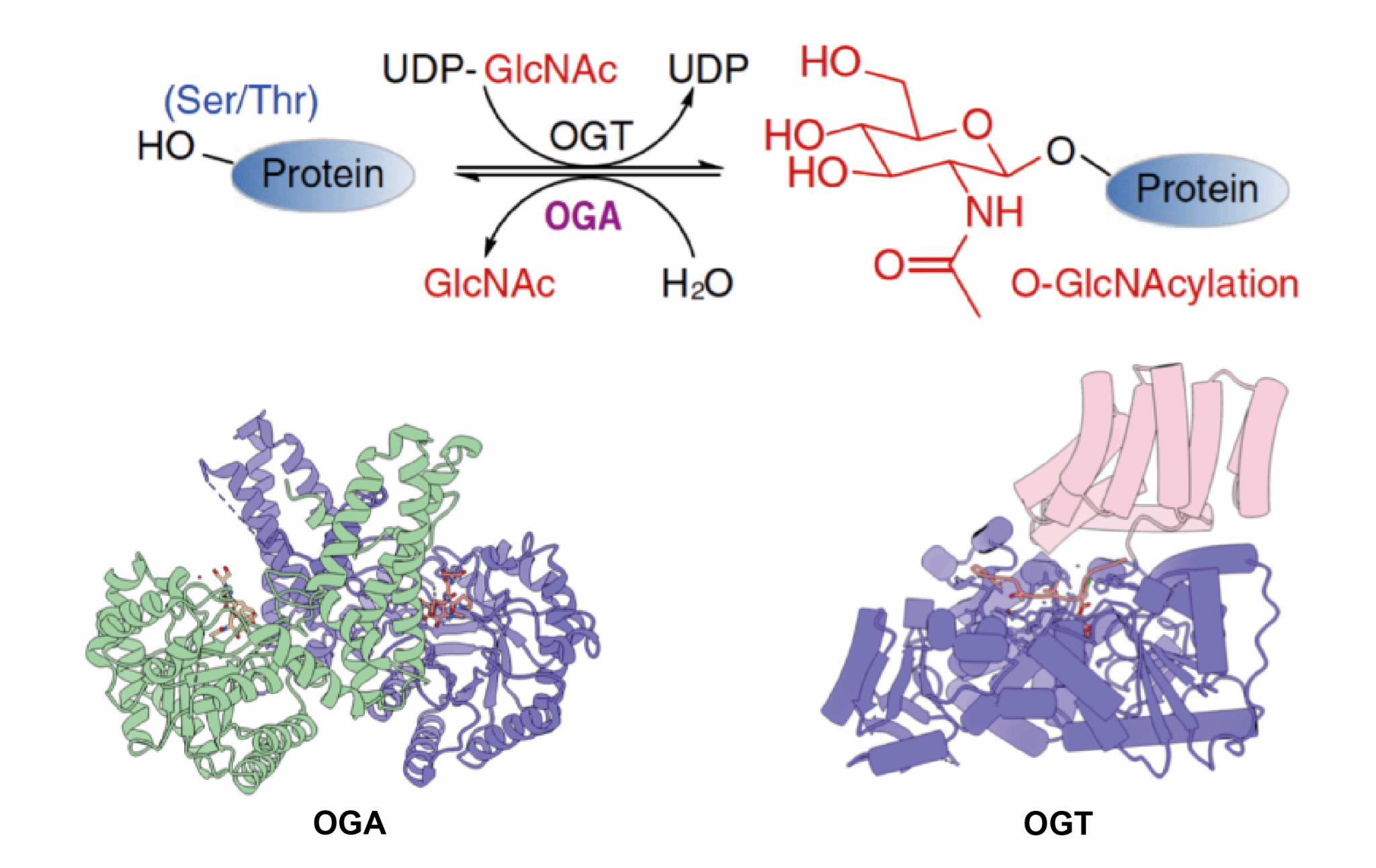
O-GlcNAcylation, an important post-translational modification, plays a protective role in Alzheimer’s disease by preventing neuronal apoptotic necrosis induced by tau aggregation. To elucidate the specificity of substrate recognition and binding in O-GlcNAcylation, as well as the inhibition mechanisms of small-molecule inhibitors, we resolved the structure of O-GlcNAcase (OGA) and its inhibitor-bound complex. Building on the 3D structure of O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) that we determined, we further developed an electrophilic probe capable of rapidly identifying key amino acid residues involved in substrate binding.
This work advances our understanding of O-GlcNAcylation as a critical regulatory modification and highlights its potential as a novel therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. It also provides an important foundation for the rational design and development of new treatments.