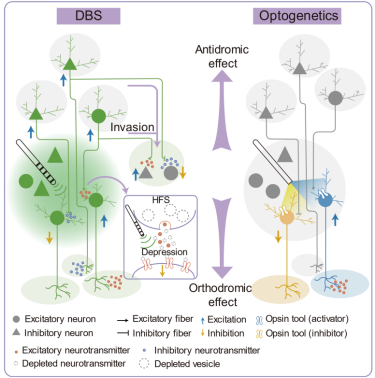
The review titled “Neuronal and synaptic adaptations underlying the benefits of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease” systematically summarizes the latest research progress in deciphering the mechanisms of deep brain stimulation (DBS) therapy using optogenetics and electrical stimulation methods. It elucidates the regulatory effects of DBS at different levels, aiming to derive the fundamental principles of DBS technology in intervening neural activity and provide a theoretical basis for studying the development of DBS. DBS can influence neurons' cell bodies and regulate local neurons' discharge patterns through the electric fields generated by implanted electrodes (Local effects). As an electrical stimulation-based neural modulation technique, it can also affect the activity of axon terminals and neural fibers circulating around the electrodes and propagate along neuronal structures in orthodromic, antidromic, and "invasive" manners, thereby modulating the activity of neurons in distant areas (Orthodromic and antidromic effects). Furthermore, due to the differences in the distribution and circuit connections of neuron subpopulations located in the target areas, the therapeutic effects of DBS are often influenced by the location of the electrodes (Position-dependent effects). Adjusting the parameters and programs of DBS can improve therapeutic effects and achieve long-term effects (Programming dependent effects). This review article was published in "Translational Neurodegeneration" in November 2023.