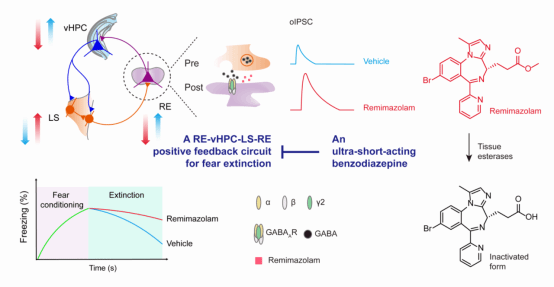
This article investigates the effects of the benzodiazepine anesthetic remimazolam on fear extinction mechanisms. Using whole-brain immunohistochemistry, electrophysiological studies, and optogenetic techniques, the research team examined its regulatory effects at the neuronal, synaptic, and neural circuit levels. The research team found that remimazolam reduces neuronal activity in the thalamic nucleus reuniens (RE) and ventral hippocampus (vHPC), reconfiguring activity in brain regions related to fear extinction and thus hindering the extinction process. Molecularly, remimazolam enhances GABA(A) receptor activity, promoting GABAergic synaptic transmission in the RE and reducing RE neuron excitability. In the term of circuit basis, remimazolam mainly targets the RE neurons projecting to the vHPC (RE-vHPC projection neurons) to achieve its regulatory effect on fear extinction. These findings provide new evidence to resolve the conflict between benzodiazepine anxiolytic treatment and exposure therapy in treating anxiety disorders and PTSD. This article was published in the "Communications Biology" in June 2024.